Morse Code¶
Description¶
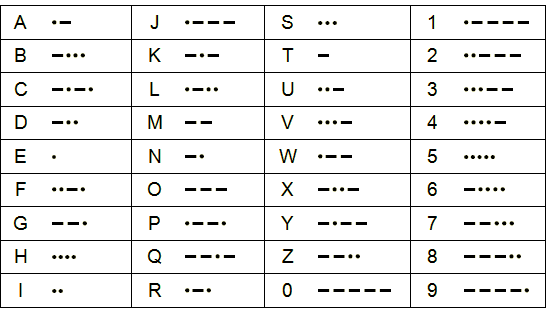
Morse code was invented in 1836 by a group of people including the American artist Samuel F. B. Morse. Using Morse code a message is represented as a series of electrical pulses which can be sent along wires to an electromagnet at the receiving end of the system. The symbols used for each letter are shown in the figure below.
Of course, you aren’t limited to electrical pulses, you can transmit a Morse code message using light or even sound. A Morse code message sent over electrical wires is known as a telegram - a message translated to Morse code by an operator at the sending end using a a telegraph key like the one pictured here.
The message is converted back to normal text by another operator at the receiving end.
Your goal is to turn your micro:bit into a machine that can encode messages using Morse code. We will call the message to be converted plain text. You will need to store the alphabet with the morse code in your program. You can use a python dictionary to do this. Here is part of a python dictionary for morse code:
morse_code = { 'A':'.-',
'B':'-...',
'C':'---.',
... }
In English, this means: the character ‘A’ should be substituted with the string ‘.-‘; the character ‘B’ should be substituted with the string ‘-…’ and so on. You can print a dictionary using:
print(morse_code)
Try this out, experiment using the REPL.